As the buzz around Web3 continues to grow, it’s easy to see why people might conflate blockchain with Web3. After all, the two terms are often mentioned together, and blockchain technology forms the backbone of Web3’s ecosystem. But while blockchain and Web3 are connected, they are not the same thing.
Think of blockchain as a foundational technology—like bricks used to build a house—while Web3 is the house itself. Blockchain provides the tools and infrastructure, and Web3 uses these tools to create a decentralized ecosystem where individuals can own their data, assets, and interactions.

In this blog, we’ll explore the difference between blockchain and Web3, clarify their roles, and demonstrate how Web3 is more than just blockchain. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of why Web3 is an ecosystem and how it leverages blockchain technology to create a user-focused internet.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a groundbreaking technology that serves as a digital ledger to securely record transactions and information. It operates on a decentralized network, meaning there is no central authority controlling or managing the system. Instead, it relies on multiple participants, called nodes, to maintain and validate the data.
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Decentralization: Data is stored across a network of nodes rather than a single server.
- Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Transparency: Transactions are recorded on a public ledger, providing visibility to all participants.
- Security: Blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
Blockchain has transformed industries by providing a secure, transparent, and efficient way to record transactions, track assets, and execute agreements.
What Is Web3?
Web3, often referred to as the “decentralized internet,” is an ecosystem built on blockchain technology that aims to give users more control over their digital lives. Web2—the current phase of the internet—is dominated by centralized platforms, where large companies own and profit from user data. Web3 seeks to change this by decentralizing control and empowering users.
Key Features of Web3:
- User Ownership: Users control their data, digital identities, and assets.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): Apps run on decentralized networks, removing the need for intermediaries.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing agreements automate processes securely.
- Tokenization: Digital assets and rewards incentivize user participation.
- Privacy and Security: Web3 enhances online privacy through encryption and decentralized identity systems.
Web3 goes beyond blockchain by integrating tools, technologies, and principles to create a new internet ecosystem. While blockchain powers Web3, the two are not interchangeable.
How Blockchain Powers Web3
Blockchain acts as the backbone of Web3, providing the infrastructure for decentralization, transparency, and security. Here’s how blockchain supports Web3’s key elements:
1. Decentralized Data Storage Web3 applications rely on decentralized storage systems to manage data securely and efficiently. Blockchain ensures data is distributed across nodes, reducing the risk of breaches or central failures.
Example: Platforms like Filecoin and Arweave use blockchain to store files in a decentralized manner, ensuring they are tamper-proof and accessible.
2. Smart Contracts for Automation Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded on a blockchain. They enable Web3 applications to automate processes like payments, identity verification, and access permissions without intermediaries.
Example: A rental agreement on Web3 could use a smart contract to release payment automatically once the renter confirms receipt of the keys.
3. Tokenized Incentives Blockchain enables the creation of digital tokens to reward users for participation and contributions. These tokens can represent ownership, access, or voting rights within a Web3 ecosystem.
Example: Decentralized social media platforms like Lens Protocol reward users with tokens for content creation and engagement.
Differences Between Blockchain and Web3
To better understand why blockchain and Web3 are not the same, let’s look at their distinctions:
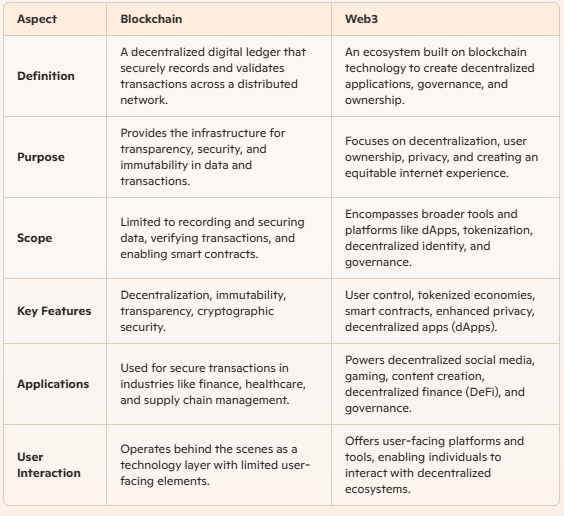
| Aspect | Blockchain | Web3 |
| Definition | A decentralized technology for recording and verifying transactions securely. | An ecosystem built on blockchain technology, enabling decentralized applications, governance, and user ownership. |
| Purpose | Acts as the infrastructure for transparency, immutability, and security. | Provides a decentralized internet experience focused on user control and autonomy. |
| Scope | Limited to specific functions like data validation, recording, and securing transactions. | Encompasses broader concepts like dApps, tokenization, decentralized governance, and privacy. |
| Applications | Used in industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain for secure record-keeping. | Powers decentralized ecosystems for social media, gaming, education, content creation, and more. |
| User Interaction | Often works behind the scenes as an infrastructure layer. | Offers user-facing tools and platforms for interaction, like decentralized wallets and applications. |
While blockchain is the foundation, Web3 builds on it to create a diverse and user-centric ecosystem.
Web3’s Expanding Ecosystem
Web3 leverages blockchain to deliver creative, empowering, and inclusive solutions across various industries. Let’s explore some examples:
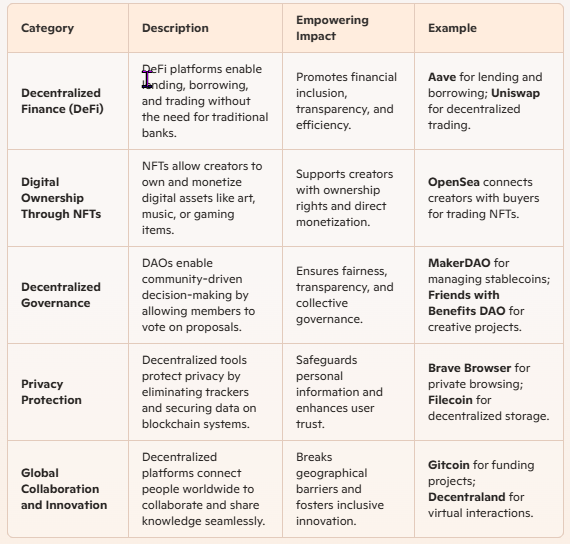
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) DeFi platforms like Aave and Uniswap enable users to lend, borrow, and trade assets without relying on traditional banks. Blockchain ensures transparency and automation through smart contracts.
2. Digital Ownership Through NFTs NFTs allow creators to own and monetize digital assets like art, music, and gaming items. Web3 platforms like OpenSea connect creators directly with buyers, fostering a fairer creative economy.
3. Decentralized Governance Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) use blockchain to enable community-driven decision-making. Members vote on proposals, ensuring transparency and fairness.
4. Privacy Protection Web3 applications like Brave Browser enhance privacy by eliminating trackers and storing user data securely on blockchain systems.
5. Global Collaboration and Innovation Web3 encourages collaboration by removing geographical barriers. Decentralized platforms connect people worldwide to innovate, share knowledge, and build projects collectively.
Why the Distinction Matters
Understanding the difference between blockchain and Web3 is crucial for appreciating the full potential of decentralized technologies. While blockchain provides the technical infrastructure, Web3 represents a vision for a user-centered internet. By recognizing this distinction, we can focus on how these technologies work together to empower individuals, transform industries, and create new opportunities.
Conclusion: Beyond a Common Misconception
The misconception that blockchain equals Web3 oversimplifies their relationship. Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that enables decentralization, transparency, and security, while Web3 is an ecosystem that builds on these principles to offer new layers of functionality, creativity, and user control.
Web3’s potential to redefine the internet is immense, and it depends on blockchain as its foundation. However, its scope extends far beyond infrastructure, shaping a decentralized future where users have ownership, privacy, and autonomy. By understanding how blockchain and Web3 work together, we can embrace the full promise of this transformative era.
Curious to learn more about Web3 and blockchain’s role in shaping the future of the internet? Subscribe to Web3WondersUS today for insights, tips, and updates on the decentralized revolution. Together, we can explore the next generation of the web!