Passive income is a fantastic way to grow your wealth without constant effort, and in the world of cryptocurrency, staking is one of the most popular methods. Staking allows you to earn rewards by locking up your cryptocurrency to support blockchain networks. In this updated guide, we’ll explain staking, its benefits, and how it compares to traditional finance (TradFi). Plus, we’ll include a helpful table of platforms offering staking, the stablecoins they support, and key details to get you started.
What Is Staking?
Staking involves locking up your cryptocurrency in a blockchain network to help validate transactions and maintain security. In return, you earn rewards, typically in the form of additional cryptocurrency. Think of it as similar to earning interest on a savings account in TradFi, but with higher potential returns.
How Does Staking Work?
Here’s how staking works:
- Choose a Cryptocurrency: Not all cryptocurrencies support staking. Popular ones include Ethereum (ETH), Cardano (ADA), and Solana (SOL).
- Select a Platform: Use a staking platform or wallet to stake your crypto.
- Lock Your Crypto: Deposit and stake your chosen cryptocurrency.
- Earn Rewards: Receive rewards based on the network’s rules and your staked amount.
Benefits of Staking
Staking offers several advantages:
- Passive Income: Earn rewards without actively trading.
- Network Security: Support blockchain operations and security.
- Potential Growth: Benefit from both staking rewards and potential price appreciation.
- Energy Efficiency: Proof-of-stake (PoS) networks are more eco-friendly than proof-of-work (PoW) systems.
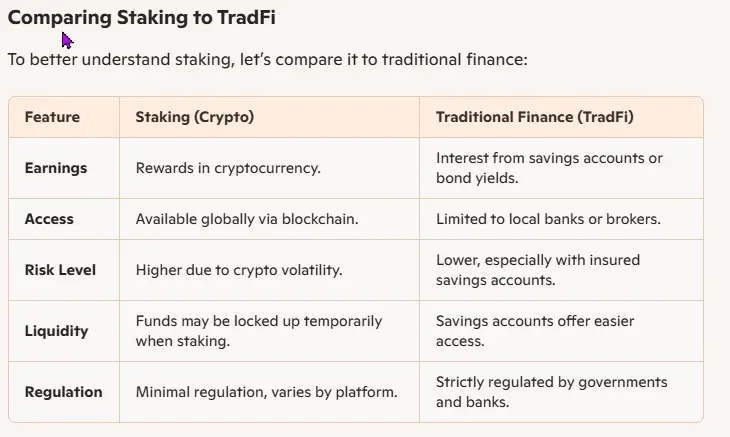
Comparing Staking to TradFi
To better understand staking, let’s compare it to traditional finance:
| Feature | Staking (Crypto) | Traditional Finance (TradFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Earnings | Rewards in cryptocurrency. | Interest from savings accounts or bond yields. |
| Access | Available globally via blockchain. | Limited to local banks or brokers. |
| Risk Level | Higher due to crypto volatility. | Lower, especially with insured savings accounts. |
| Liquidity | Funds may be locked up temporarily when staking. | Savings accounts offer easier access. |
| Regulation | Minimal regulation, varies by platform. | Strictly regulated by governments and banks. |
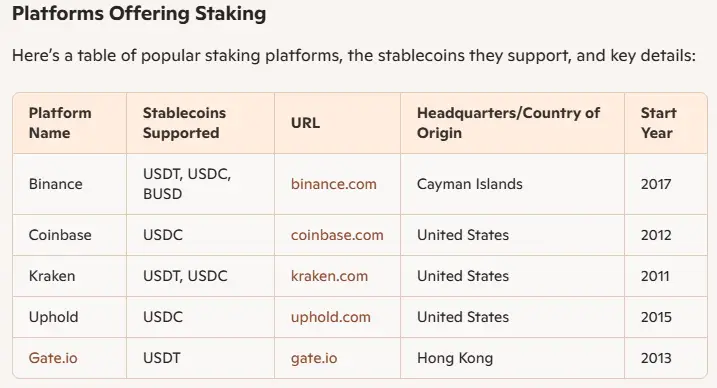
Platforms Offering Staking
Here’s a table of popular staking platforms, the stablecoins they support, and key details:
| Platform Name | Stablecoins Supported | URL | Headquarters/Country of Origin | Start Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binance | USDT, USDC, BUSD | binance.com | Cayman Islands | 2017 |
| Coinbase | USDC | coinbase.com | United States | 2012 |
| Kraken | USDT, USDC | kraken.com | United States | 2011 |
| Uphold | USDC | uphold.com | United States | 2015 |
| Gate.io | USDT | gate.io | Hong Kong | 2013 |
How to Get Started with Staking
- Choose a Platform: Select a trusted platform from the table above.
- Research Reward Rates: Compare staking rewards to maximize your earnings.
- Understand Lock-Up Terms: Some platforms require you to lock your crypto for a set period.
- Start Small: Begin with a small amount to minimize risk.
Risks to Consider
While staking is a great way to earn passive income, it’s not without risks:
- Volatility: The value of your staked crypto can fluctuate.
- Lock-Up Periods: Your funds may be inaccessible during staking.
- Platform Security: Use reputable platforms to avoid scams or hacks.
Call to Action: Learn More with Web3Wonders
Staking is just one of the many ways to earn passive income in the world of Web3. At Web3Wonders.US, we simplify complex topics like staking to help beginners succeed in blockchain and cryptocurrency.
Subscribe now to join our community and access exclusive guides, tips, and insights about earning with cryptocurrency and Web3 tools. Take the first step toward mastering crypto staking and creating a smarter financial future!
Disclaimer: The information in this blog is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Investing in Traditional Finance and Web 3 assets, including cryptocurrencies and precious metals, involves significant risks, including the potential loss of principal. Always conduct your own research and consult a qualified financial advisor and/or tax advisor before making investment decisions. Past performance is not indicative of future results.


45bet is another one that I keep around for a bit of a play. It’s quite alright. Here you go, this is where where I like to unwind:45bet.
Sup folks! jljl533 looks legit enough. Have a gander at jljl533
For lottery players, lottuse has some interesting options. Worth checking out if you want to try your luck. Good luck: lottuse
Bora ganhar dinheiro, galera! Descobri a brganhar777 e tô apostando em tudo que posso. Tem odds boas e umas promoções bem agressivas. Foco, força e fé pra gente faturar alto!
N8casino is my go-to spot for some online gambling fun. They have a wide variety of games and the payouts are pretty decent too. Check out them from n8casino if you are looking for a good time.
ffwinbet, huh? Gave her a glance. Looks decent enough. If you’re looking to place a bet or two, might be worth having a look-see. Remember to bet responsibly though! Link’s here: ffwinbet.
Vaobong88com is my go-to when I can’t access the main site. Never had any issues, always a smooth and quick connection. Definitely a bookmark to have! vaobong88com